The History of Artificial Intelligence, Generative AI & Chat GPT
The History of Artificial Intelligence, Generative AI & Chat GPT
If you want to understand the future of AI, consider its past.
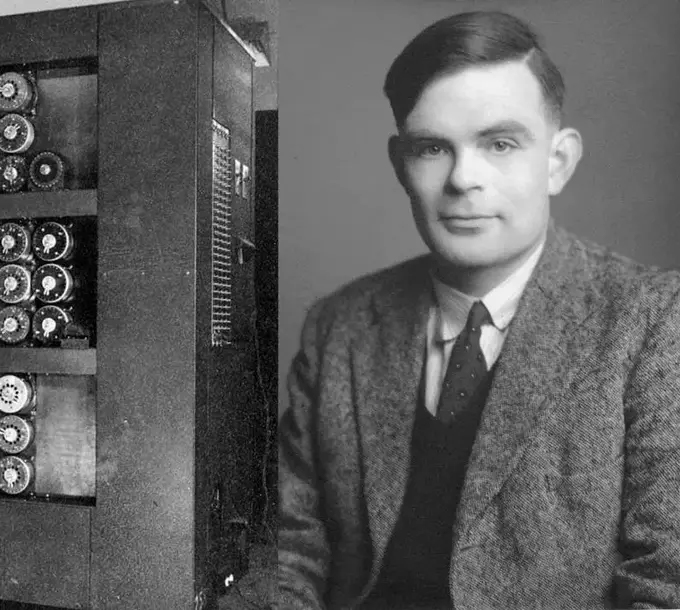
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a dynamic and ever emerging branch of computer science that refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines or computer programs. From Alan Turing’s pioneering work in the 1940s to John McCarthy’s coining of the term “artificial intelligence” in 1955, AI has steadily advanced, surviving its ‘winters’ of reduced enthusiasm to emerge as a transformative force in the 21st century.
Key Historical Dates
Antiquity: Ancient myths and stories feature artificial beings with human-like intelligence, inspiring the concept of intelligent machines.
17th-18th centuries: George Boole’s work on symbolic logic and Charles Babbage’s Analytical Engine lay the groundwork for computational thinking.
1936: Alan Turing’s paper, “On Computable Numbers,” introduces the concept of the Turing machine, a theoretical foundation for modern computing and AI.
1943: Warren McCulloch and Walter Pitts publish a paper on neural networks, laying the groundwork for artificial neurons.
1950: Alan Turing publishes “Computing Machinery and Intelligence,” which introduces the concept of the Turing Test for assessing machine intelligence.
1955: John McCarthy coins the term “artificial intelligence” (AI) and organizes the Dartmouth Workshop, often considered the birth of AI as a field.
1956: The Dartmouth Workshop becomes the first-ever conference on AI, marking the formal beginning of AI research.
1956-1969: The early years of AI research are marked by optimism and significant developments in symbolic AI.
1957: Frank Rosenblatt develops the perceptron, an early model of artificial neural networks.
1958: John McCarthy invents the LISP programming language, which becomes crucial in AI research.
1965: Joseph Weizenbaum creates ELIZA, one of the first chatbot programs.
1967: Dendral, an expert system for chemical analysis, is developed, showcasing the potential of expert systems.
1970: The Stanford Cart becomes one of the first mobile robots capable of navigating autonomously.
1973: The Lighthill Report in the UK criticizes the progress in AI research, leading to a funding decrease, referred to as the “AI winter.”
1974: Ted Shortliffe develops MYCIN, a rule-based expert system for diagnosing bacterial infections.
1980: John Hopfield introduces Hopfield networks, a form of recurrent artificial neural networks.
1983: Japan launches the Fifth Generation Computer Systems project, with a focus on AI and parallel processing.
1984: David Rumelhart, Geoffrey Hinton, and Ronald Williams publish a paper on backpropagation, a critical development in neural network training.
1985: Terry Sejnowski and Charles Rosenberg publish the NETtalk paper, demonstrating neural network-based speech recognition.
1988: Yann LeCun introduces Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), revolutionizing computer vision.
1990: Douglas Lenat’s CYC project begins an ambitious effort to create a comprehensive AI knowledge base.
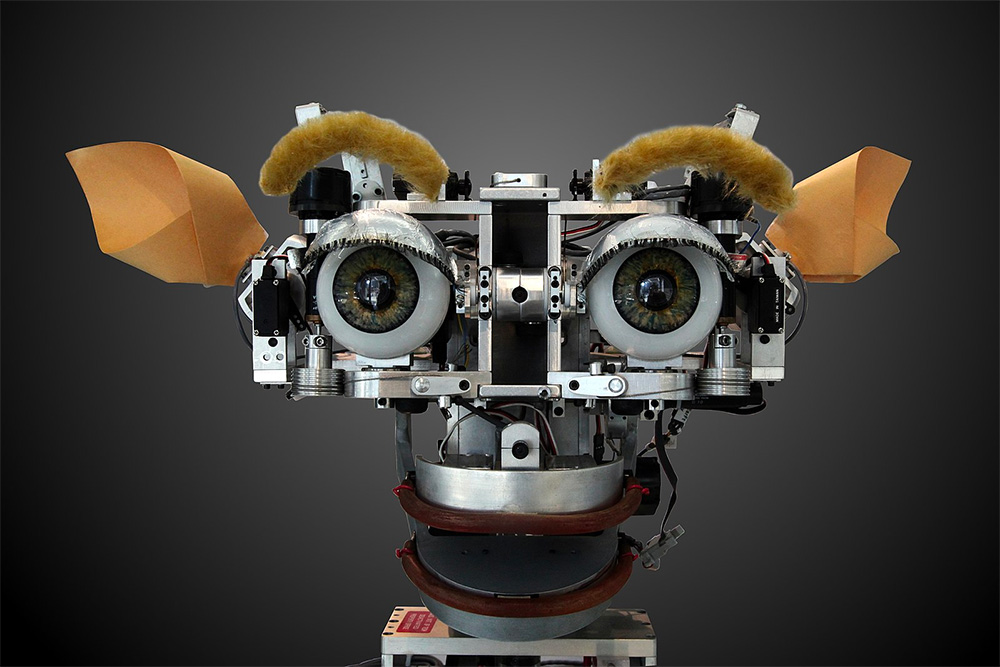 1993: Kismet was a robot head which was made in the 1990s at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) by Dr. Cynthia Breazeal as an experiment in affective computing; a machine that can recognize and simulate emotions. The name Kismet comes from a Turkish word meaning “fate” or sometimes “luck”
1993: Kismet was a robot head which was made in the 1990s at Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) by Dr. Cynthia Breazeal as an experiment in affective computing; a machine that can recognize and simulate emotions. The name Kismet comes from a Turkish word meaning “fate” or sometimes “luck”
1996: IBM’s Deep Blue defeats Garry Kasparov, the world chess champion, in a six-game match.
1997: IBM’s Deep Blue defeats Garry Kasparov again in a rematch, demonstrating AI’s capability in complex strategy games.
2001: Wikipedia is launched, providing a valuable resource for training natural language processing algorithms.
2011: IBM’s Watson defeats human champions in the quiz show Jeopardy!, showcasing advancements in natural language understanding.
2012: Geoffrey Hinton and his team win the ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge with a deep convolutional neural network.
2014: Facebook AI Research (FAIR) is established, contributing to advancements in deep learning and computer vision.
2016: AlphaGo, developed by DeepMind, defeats Lee Sedol, a world Go champion, marking a significant achievement in AI and board games.
2017: GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) models are introduced, revolutionizing natural language processing.
2018: OpenAI’s GPT-2 model generates significant attention for its text generation capabilities. OpenAI introduces reinforcement learning algorithms like Proximal Policy Optimization.
2019: Google achieves quantum supremacy with its quantum computer, potentially impacting AI through faster computations.
2020: DeepMind’s AlphaFold demonstrates remarkable success in predicting protein structures, aiding in drug discovery.
2021: OpenAI’s GPT-3 model becomes widely discussed for its natural language understanding and generation capabilities. OpenAI’s ChatGPT is released, allowing for text-based conversations with AI.
2021: Researchers at Facebook AI develop CLIP, a model that understands images and text together.
2022: OpenAI unveils the ChatGPT API, making it accessible for developers and businesses. OpenAI introduces DALL-E, a model capable of generating images from textual descriptions.
2022: OpenAI announces the GPT-4 architecture, showcasing ongoing advancements in AI research.
2022: AI continues to advance, with ongoing developments in ethical AI, AI for healthcare, and applications in various industries.
2023: Quantum computing research continues, with potential implications for AI and machine learning.
2023: AI ethics and regulations become increasingly important topics in the field.
Recent History of AI, Generative AI, and Chat GPT (2015 to Present):
The history of artificial intelligence (AI), generative AI, and models like ChatGPT from 2015 to the present is marked by rapid developments and significant milestones. Here’s an overview of the key events and advancements:
2015-2016: Early Deep Learning Breakthroughs
- 2015: The resurgence of neural networks, thanks to deep learning, started gaining momentum. Key advancements in image recognition, natural language processing (NLP), and generative models were noted.
- AlphaGo: In 2016, DeepMind’s AlphaGo defeated world champion Go player Lee Sedol, a landmark event demonstrating the potential of deep learning in complex problem-solving.
2017-2018: Rise of Transformers and NLP
- Transformers: The introduction of the Transformer architecture in 2017 by Vaswani et al. revolutionized NLP. Its self-attention mechanism enabled more effective handling of sequential data compared to previous models like RNNs and LSTMs.
- BERT: In 2018, Google introduced BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), a groundbreaking NLP model that significantly improved the understanding of context in language.
2019-2020: Generative Models and GPT-2
- GPT-2: OpenAI introduced GPT-2 in 2019, a large transformer-based language model known for its ability to generate coherent and contextually relevant text over extended passages. Its release was initially staggered due to concerns about potential misuse.
- Generative Models: This period also saw advancements in other generative models like VAEs (Variational Autoencoders) and GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), particularly in image and video generation.
2020: GPT-3 and the AI Explosion
- GPT-3: OpenAI released GPT-3, an even larger and more powerful model than GPT-2, with 175 billion parameters. GPT-3 demonstrated an unprecedented ability to generate human-like text, perform language translation, and even code generation, sparking widespread interest and applications in AI.
- AI Ethics and Accessibility: With the power of GPT-3, discussions around AI ethics, bias, and accessibility became more prominent. OpenAI and other organizations began to focus more on the responsible deployment of AI technologies.
 2022-2023: Generative AI and Beyond
2022-2023: Generative AI and Beyond
- Generative AI Expansion: The field saw the expansion of generative AI beyond text to include images, audio, and multimodal AI systems. Models like DALL-E, which generates images from textual descriptions, and Whisper, an automatic speech recognition system, showcased the versatility of generative AI.
- ChatGPT and Codex: OpenAI introduced ChatGPT, based on the GPT-3.5 architecture, optimized for conversational responses, and Codex, which powers GitHub Copilot, offering assistance in code generation and explanation.
- AI in Society: AI applications became more embedded in various sectors, including healthcare, finance, creative arts, and education. The societal impact, including job displacement and new job creation, became a significant topic of discussion.
2024: The Cutting Edge and Future Directions
- Advancements in AI Models: Continual improvements in model architectures, training techniques, and efficiency. Efforts in making AI more interpretable, ethical, and less resource-intensive are ongoing.
- AI Governance and Policy: With AI becoming more influential in daily life, the formulation of policies and frameworks for its ethical and equitable use is a key focus for governments and international bodies.
This overview highlights the rapid evolution of AI, particularly in generative models and conversational AI like ChatGPT. The field continues to evolve, driven by both technological advancements and societal needs.
MORE:
Detailed History of Artificial Intelligence (AI) »
Detailed TIMELINE of Artificial Intelligence (AI) »
History & Background of Generative Artificial Intelligence (AI) »
History of Natural Language Processing »
Progress of AI: From Chess to Exams to Predictions of the Future »
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)? »
Main Image Source: Wikimedia Commons | Robot Head: Wikimedia Commons | Astronaut on Horse: Wikimedia Commons
Content sources: Original | Generative AI | Wikipedia